My cousin once asked me what I thought about deciding on who to vote for for President might be best done when evaluating how well your 401K or investments did. Kind of an amusing thought. In that vein the decisions might be very different than they were. Clearly your 401k did with with Clinton. The economy was flat for George W. Bush, and the end of his term was the Great Recession. Reagan’s first term was flat. We all know about George H.W. Bush. Interesting thoughts. Not so good. So what about the last 8 years? But is raises a more interesting issue. So don’t get me wrong, this blog is not intended to lobby for any candidate (and Obama can’t run), but it is interesting to look at the last 8 years. They have been difficult. The economy responded slowly. Wages did not rebound quickly. But in comparison to 2008 are we better off?
The question has relevance for utilities because if our customers are better off, that gives us more latitude to do the things we need – build reserves (so we have funds for the next recession), repair/replace infrastructure (because unlike fine wine, it is not improving with age), improve technology (the 1990s are long gone), etc., all things that politicians have suppressed to comport with the challenges faced by constituents who have been un- or under-employed since 2008.
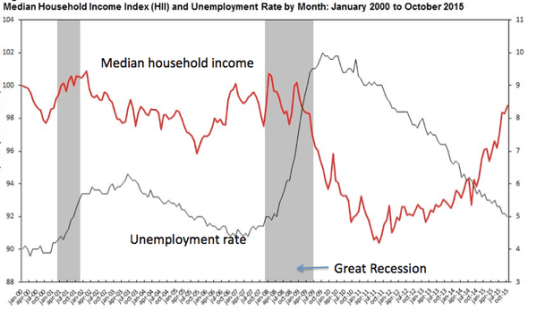
Economist Paul Krugman makes an interesting case in a recent op-ed in the New York times: (http://krugman.blogs.nytimes.com/2016/01/13/yes-he-did/?module=BlogPost-Title&version=Blog%20Main&contentCollection=Opinion&action=Click&pgtype=Blogs®ion=Body). Basically he summarizes the figure below which shows that unemployment is back to pre-2008 levels, and income is back to that point. Some income increase would have been good, but this basically tracks with the Bush and Reagan years for income growth – flat. So the question now is in comparison to 2008 are we worse off that we were? And if not, can we convince leaders to move forward to meet our needs? Can we start funding some of the infrastructure backlog? Can we modernize? Can we create “smarter networks?” Can we adjust incomes to prevent more losses of good employees? Can we improve/update equipment? All issues we should contemplate in the coming budget.