For your Reading Pleasure….
http://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2016/03/flint-task-force-rick-snyder-blame/475182/
http://www.vindy.com/news/2016/mar/20/few-knew-of-excess-lead-in-warrens-water/?mobile
How to Predict the next Flint?
 In the last blog we talked about Flint’s water quality problem being brought on by a political/financial decision, not a public health decision. Well, the news get worse. Flint’s deteriorated water system is a money thing as well – the community has a lot of poverty and high water bills, so they can’t pay for improvements. They are not alone. Utilities all over the country have increasing incidents of breaks, and age related problems. So the real question then is who are the at risk utilities? Who is the next Flint? It would be an interesting exercise to see if a means could be developed to identify those utilities at risk for future crises, so we can monitor them in more detail as a means to avoid such crises.
In the last blog we talked about Flint’s water quality problem being brought on by a political/financial decision, not a public health decision. Well, the news get worse. Flint’s deteriorated water system is a money thing as well – the community has a lot of poverty and high water bills, so they can’t pay for improvements. They are not alone. Utilities all over the country have increasing incidents of breaks, and age related problems. So the real question then is who are the at risk utilities? Who is the next Flint? It would be an interesting exercise to see if a means could be developed to identify those utilities at risk for future crises, so we can monitor them in more detail as a means to avoid such crises.
So what would be the measures that might identify the future “Flint?” These could be things like age of the system, materials used, economic activity trends, income, poverty rate, unemployment rate, utility size, reserves, utility rates, history of rate increases, etc.? Could these be developed into a means to evaluate risk? If so, who would use it and how would we address the high risk cases? I suggest that lenders have means to evaluate this using many of these same measures, but from a risk of events, this method has not been applied. So I think this would be a useful research project. So if anyone has some ideas, time or ideas for funding, let me know. Let’s get rolling!
Speaking of water supply problems, welcome to Flint, Michigan. There have been a lot of coverage in the news about the troubles in Flint the last couple of months. However if you read between the lines you see two issues – first this is not new – it is several years old, going back to when the City’s water plant came back on line in May 2014. Second this was a political/financial issue not a public health issue. In fact, the political/financial goals appear to have been so overwhelming, that the public health aspects were scarcely considered. Let’s take a look at why.
Flint’s first water plant was constructed in 1917. The source was the Flint River. The second plant was constructed in 1952. Because of declining water quality in the Flint River, the city, in 1962, had plans to build a pipeline from Lake Huron to Flint, but a real estate scandal caused the city commission to abandon the pipeline project in 1964 and instead buy water from the City of Detroit (source: Lake Huron). Flint stopped treating its water in 1967, when a pipeline from Detroit was completed. The City was purchasing of almost 100 MGD. Detroit declared bankruptcy. The City of Flint was basically bankrupt. Both had appointed receivers. Both receivers were told to reduce costs (the finance/business decisions). The City of Flint has purchased water for years from Detroit as opposed to using their Flint River water plant constructed in 1952. The Flint WTP has been maintained as a backup to the DWSD system, operating approximately 20 days per year at 11 MGD.
The City of Flint joined the Karegnondi Water Authority (KWA) in 2010. The KWA consists of a group of local communities that decided to support and fund construction of a raw water pipeline to Lake Huron. The KWA was to provide the City of Flint Water Treatment Plant with source water from Lake Huron. An engineer’s report noted that a Genesee County Drain Commissioner stated that one of the main reasons for pursuing the KWA supply was the reliability of the Detroit supply given the 2003 power blackout that left Flint without water for several days. Another issue is that Flint no say in the rate increases issued to Flint by Detroit. Detroit’s bankruptcy may also have been a factor given the likelihood of increased prices. While discussion were ongoing for several years thereafter, the Detroit Free Press reported a 7-1 vote in favor of the KWA project by Flint’s elected officials in March, 2013. The actual agreement date was April 2013. The cost of the pipeline was estimated to be $272 million, with Flint’s portion estimated at $81 million.
The City of Detroit objected due to loss of revenues at a time when a receiver was trying to stabilize the city’s finances (in conjunction with the State Treasurer). In February 2013, the engineering consulting firm of Tucker, Young, Jackson, Tull, Inc. (TYJT), at the request of the State Treasurer, performed an analysis of the water supply options being considered by the City of Flint. The preliminary investigation evaluated the cost associated with the required improvements to the plant, plus the costs for annual operation and maintenance including labor, utilities, chemicals and residual management. They indicated that the pipeline cost was likely low and Flint’s obligation could be $25 million higher and that there was less redundancy in the KWA pipeline than in Detroit’s system. In 2013, the City of Detroit made a final offer to convince Flint to stay on Detroit water with certain concessions. Flint declined the final Detroit offer. Immediately after Flint declined the offer, Detroit gave Flint notice that their long-standing water agreement would terminate in twelve months, meaning that Flint’s water agreement with Detroit would end in April 2014 but construction of KWA was not expected to be completed until the end of 2016.
It should be noted that between 2011 and 2015, Flint’s finances were controlled by a series of receivers/emergency managers appointed by the Governor. Cutting costs was a major issue and clearly their directive from the Governor. Cost are the major issue addressed in the online reports about the issue. Public health was not.
An engineering firm was hired as the old Flint River plan underwent $7 million in renovations in 2014 to the filters to treat volumes of freshwater for the citizens. The project was designed to take water from the Flint River for a period of time until a Lake Huron water pipeline was completed. The City of Flint began using the Flint River as a water source in May of 2014 knowing that treatment would need to be closely watched since the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality in partnership with the U.S. Geological Survey, and the City of Flint Utilities Department conducted a source water assessment and determined the susceptibility of potential contamination as having a very high susceptibility to potential contaminant sources (take a look at this photo and see what you think).

Flows were designed for 16 MGD. Lime softening, sand filters and disinfection were in place. Everything sounded great. But it was not. Immediately, in May and August of 2014, TTHM samples violated the drinking water standards. This means two things – total organic carbon (TOC) in the water and additional chlorine being added to disinfect and probably reduce color caused by the TOC. Softening does not remove TOC. Filtration is not very effective either. High concentration usually needs granular activated carbon, ion exchange or membranes. The flint plant had none of these, so the carbon staying in the water. To address the TTHM issue, chlorine appears to have been reduced as the TTHM issue was in compliance by the next sampling event in Nov 2014. However, in the interim new violations included a total coliform and E. coli in August and September of 2014, and indication of inadequate disinfection. That means boil your water and lots of public outcry. The pH, salinity (salt) and other parameters were reported to be quite different than the Detroit water as well. A variable river system with upstream agriculture, industry and a high potential for contamination, is not nearly as easy to treat as cold lake water. These waters are very different as they City was to find. What this appears to indicate is that the chemistry profile and sampling prior to conversion and startup does not appear to have been fully performed to identify the potential for this to occur or this would have been discovered. This is now being suggested in the press.
The change in water quality and treatment created other water quality challenges that have resulted in water quality violations. Like most older northern cities, the water distribution system in almost 100 years old. As with many other municipalities at the time, all of the service lines from the cast iron water mains (with lead joints) to end users homes were constructed with lead goosenecks and copper lines. Utilities have addressed this with additive to prevent corrosion. In the early 1990s water systems were required to comply with the federal lead and copper rule. The concept was that on the first draw of water in the morning, the lead concentration should not exceed 0.015 mg/L and copper should not exceed 1.3 mg/L. Depending on the size of the utility, sampling was to be undertaken twice and a random set of hoses, with the number of samples dependent on the size of the system. The sampling was required to be performed twice, six months apart (note routine sampling has occurred since then to insure compliance). Residents were instructed on how to take the samples, and results submitted to regulatory agencies. If the system came up “hot” for either compound, the utility was required to make adjustments to the treatment process. Ideally water leaving the plant would have a slightly negative Langlier saturation index (LSI) and would tend to slightly deposit on pipes. Coupon tests could be conducted to demonstrate this actually occurred. As they age, the pipes develop a scale that helps prevent leaching. Most utilities tested various products. Detroit clearly did this and there were no problems. Flint did not.
The utility I was at was a perfect 100% non-detects the first time were tested. We had a few detections of lead and copper in samples the second time which really bothered me since the system was newer and we had limited lead in the lines. I investigated this and found that the polyphosphate had been changed because the County purchasing department found a cheaper product. I forced them to buy the old stuff, re-ran the tests and was again perfect. We instructed our purchasing department that saving a few bucks did not protect the public health, but the polyphosphate product did. Business and cost savings does not trump public health! Different waters are different, so you have to test and then stay with what works.
Now fast forward to Flint. They did not do this testing. The Flint River water was different that Detroit’s. Salinity, TOC, pH and overall quality differed. Accommodations were not made to address the problem and the state found no polyphosphates were added to protect the coatings. Veolia reported that the operations needed changes and operators needed training. Facilities were needed to address quality concerns (including granular activated carbon filter media). As a result the City appears to have sent corrosive water into the piping system, which dissolved the scale that had developed over the years, exposing raw metal, and created the leaching issue. Volunteer teams led by Virginia Tech researchers reported found that at least a quarter of Flint households have levels of lead above the federal level of 15 ppb, and as high as 13,200 ppb. Aging cast-iron pipe compounded the situation, leading to aesthetic issues including taste, odor and discoloration that result from aggressive water (brown water). Once the City started receiving violations, public interest and scrutiny of the drinking water system intensified.
The City Commission reportedly asked the receiver to switch back to Detroit water, but that request was initially rebuffed and the damage to pipes continued. Finally in October 2015, the water supply was switched back to Detroit and the City started adding additional zinc orthophosphate in December 2015 to facilitate the buildup of the phosphate scale eroded from the pipes by the Flint River water. But that means the pipes were stable, then destabilized, now destabilized again by the switch back. It will now take some time for the scale to rebuild and to lower lead levels, leaving the residents of Flint at risk because of a business/finance/political decision that had not consideration of public health impacts. And what is the ultimate fate of the KWA pipeline?
Just when things were starting to look up (?), in January 2016, a hospital in Flint reported that low levels of Legionnaires’ disease bacteria were discovered in the water system and that 10 people have died and another 77 to 85 affected. From the water system? A disinfection problem? Still TOC in the water? The lawsuits have begun but where does the problem lie? Let’s look at Walkerton Ontario for guidance in the aftermath of their 2000 incident.
First it is clear that public health was not the primary driver for the decisions. Treating water is not as simple as cost managers think. You need to understand what water quality, piping quality and stabilization you have and address the potential issues with new water sources. Membrane systems are very familiar with these challenges. Cost cannot be the driver. The Safe Drinking Water Act does not say cost is a consideration you use to make decisions. Public health is. So the initial decision-making appears to have been flawed. Cost was a Walkerton issue – cost cannot be the limiting factor when public health is at risk.
The guidance from consultants or other water managers is unclear. If the due diligence of engineers as to water quality impacts of the change in waters was not undertaken, the engineering appears to have been flawed. If the engineer recommended, and has lots of documentation saying testing should be done, but also a file full of accompanying denials from the receivers, another flawed business decision that fails the public health test. If not, I see a lawsuit coming against the consultants who failed in their duty to protect the public health, safety and welfare.
The politics is a problem. A poor community must still get water and sewer service. Consultants that can deal with rate and fee issues should be engaged to address fairness and pricing burdens. Was this done? Or was cutting costs the only goal? Unclear. The politics was a Walkerton issue.
Was the water being treated properly? Water quality testing would help identify this. Clearly there were issues with operations. Telling the state phosphates were used when they were not, appears to be an operations error. Walkerton also had operations issues as well. A major concern when public health is at risk. Veolia came to a similar conclusion.
The state has received its share of blame in the press, but do they deserve it? The question I have is what does the regulatory staff look like? Has it been reduced as the state trims its budget? Are there sufficient resources to insure oversight of water quality? The lack of provincial resources to monitor water quality was an issue in Walkerton – lack of oversight compounded local issues. That would then involve the Governor and Legislature. Politics at work. Likewise was there pressure applied to make certain decisions? If so, politics before public heath – a deadly combination.
So many confounding problems, but what is clear is that Flint is an example of why public utilities should be operated with public health at the forefront, not cost or politics. Neither cost of politics protect the public health. While we all need finances to pay for our needs, in a utility, money supports the operations, not controls it. We seems to have that backward. Private entities look sat controlling costs. Public agencies should look at public service first; cost is down the list. We need the operations folks to get the funds needed to protect the public health. And then we need to get the politicians to work with the staff to achieve their needs, not limit resources to cut costs for political gain. Ask the people in Flint.
So is Flint the next Walkerton? Will there be a similar investigation by outside unconnected people? Will the blame be parsed out? Is there a reasonable plan for the future? The answers to these questions would provide utilities with a lot of lessons learned and guidance going forward and maybe reset the way we operate our utilities. Happy to be a part of it if so!
 One of the issues I always include in rate studies is a comparison of water rates with other basic services. Water always comes in at the bottom. But that works when everyone has access and uses those services. Several years ago a study indicated that cable tv was in 87-91 % of home. At the time I was one of the missing percentage, so I thought it was interesting. However, post the 2008 recession, and in certain communities, this may be a misplace comparison. A recent study by Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman notes that the top 0.1% have assets that are worth the same as the bottom 90% of the population! Yes, you read that correctly. Occupy Wall Street had it wrong. It’s not the 1% it is the 0.1%. This is what things were like in the 1920s, just before the Great Depression. The picture improved after the implementation of tax policies (the top tax rate until 1964 was 90% – yes you read that right – 90%). Then the tax rate was slowly reduced to deal with inflation. The picture continued to improve until supply side economics was introduced in the early 1980s when the disparity started to rise again (see their figure below), tripling since the late 1970s (you recall the idea was give wealthy people more money and they would invest it in jobs that would increase employment opportunities and good jobs for all, or something like that). Supply side economics did not/does not work (jobs went overseas), and easy credit borrowing and education costs have contributed to the loss of asset value for the middle class as they strove to meet job skills requirements for better jobs. In addition wages have stagnated or fallen while the 0.1% has seen their incomes rise. The problem has been exacerbated since 2008 as they report no recovery in the wealth of the middle class and the poor. So going back to my first observation – what gets cut from their budget, especially the poor and those of fixed pensions? Food? Medicine? Health care? My buddy Mario (86 year old), still works because he can’t pay his bills on social security. And he does not live extravagantly. So do they forego cable and cell phones? If so the comparison to these costs in rate studies does not comport any longer. It places at risk people more at risk. And since, rural communities have a lower income and education rate than urban areas, how much more at risk are they? This is sure to prove more interesting in the coming years. Hopefully with some tools we are developing, these smaller communities can be helped toward financial and asset sustainability. But it may require some tough decisions today.
One of the issues I always include in rate studies is a comparison of water rates with other basic services. Water always comes in at the bottom. But that works when everyone has access and uses those services. Several years ago a study indicated that cable tv was in 87-91 % of home. At the time I was one of the missing percentage, so I thought it was interesting. However, post the 2008 recession, and in certain communities, this may be a misplace comparison. A recent study by Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman notes that the top 0.1% have assets that are worth the same as the bottom 90% of the population! Yes, you read that correctly. Occupy Wall Street had it wrong. It’s not the 1% it is the 0.1%. This is what things were like in the 1920s, just before the Great Depression. The picture improved after the implementation of tax policies (the top tax rate until 1964 was 90% – yes you read that right – 90%). Then the tax rate was slowly reduced to deal with inflation. The picture continued to improve until supply side economics was introduced in the early 1980s when the disparity started to rise again (see their figure below), tripling since the late 1970s (you recall the idea was give wealthy people more money and they would invest it in jobs that would increase employment opportunities and good jobs for all, or something like that). Supply side economics did not/does not work (jobs went overseas), and easy credit borrowing and education costs have contributed to the loss of asset value for the middle class as they strove to meet job skills requirements for better jobs. In addition wages have stagnated or fallen while the 0.1% has seen their incomes rise. The problem has been exacerbated since 2008 as they report no recovery in the wealth of the middle class and the poor. So going back to my first observation – what gets cut from their budget, especially the poor and those of fixed pensions? Food? Medicine? Health care? My buddy Mario (86 year old), still works because he can’t pay his bills on social security. And he does not live extravagantly. So do they forego cable and cell phones? If so the comparison to these costs in rate studies does not comport any longer. It places at risk people more at risk. And since, rural communities have a lower income and education rate than urban areas, how much more at risk are they? This is sure to prove more interesting in the coming years. Hopefully with some tools we are developing, these smaller communities can be helped toward financial and asset sustainability. But it may require some tough decisions today.

My cousin once asked me what I thought about deciding on who to vote for for President might be best done when evaluating how well your 401K or investments did. Kind of an amusing thought. In that vein the decisions might be very different than they were. Clearly your 401k did with with Clinton. The economy was flat for George W. Bush, and the end of his term was the Great Recession. Reagan’s first term was flat. We all know about George H.W. Bush. Interesting thoughts. Not so good. So what about the last 8 years? But is raises a more interesting issue. So don’t get me wrong, this blog is not intended to lobby for any candidate (and Obama can’t run), but it is interesting to look at the last 8 years. They have been difficult. The economy responded slowly. Wages did not rebound quickly. But in comparison to 2008 are we better off?
The question has relevance for utilities because if our customers are better off, that gives us more latitude to do the things we need – build reserves (so we have funds for the next recession), repair/replace infrastructure (because unlike fine wine, it is not improving with age), improve technology (the 1990s are long gone), etc., all things that politicians have suppressed to comport with the challenges faced by constituents who have been un- or under-employed since 2008.
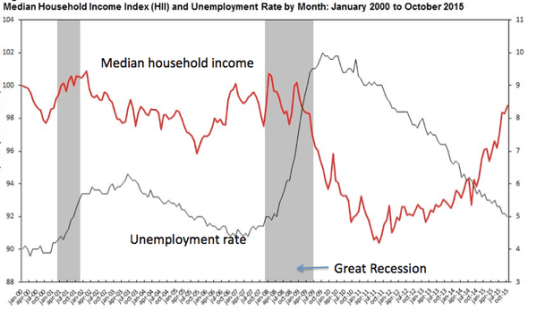
Economist Paul Krugman makes an interesting case in a recent op-ed in the New York times: (http://krugman.blogs.nytimes.com/2016/01/13/yes-he-did/?module=BlogPost-Title&version=Blog%20Main&contentCollection=Opinion&action=Click&pgtype=Blogs®ion=Body). Basically he summarizes the figure below which shows that unemployment is back to pre-2008 levels, and income is back to that point. Some income increase would have been good, but this basically tracks with the Bush and Reagan years for income growth – flat. So the question now is in comparison to 2008 are we worse off that we were? And if not, can we convince leaders to move forward to meet our needs? Can we start funding some of the infrastructure backlog? Can we modernize? Can we create “smarter networks?” Can we adjust incomes to prevent more losses of good employees? Can we improve/update equipment? All issues we should contemplate in the coming budget.
 Over the holidays there were a couple articles that came out about groundwater issues in the US, mostly from the declining water level perspective. I also read a paper that suggested that rising sea level had a contribution from groundwater extraction, and of course USGS has maps of areas where the aquifer have collapsed as a result of overpumping. In 2009 USGS published a report that showed a large areas across the country with this issue. The problem is that of the 50,000 community water systems in the US, 500 serve over 50% of the population, and most of them are surface water plants. There are over 40,000 groundwater systems, but most are under 500 customers. Hence, groundwater is under represented at with the larger water associations because the large utilities are primarily surface water, while the small systems are groundwater. AWWA has difficulty reaching the small systems while RWA and NGWA reach out to them specifically. But the small utility seems more oriented to finding and producing water and operating/maintaining/drilling wells than the bigger impact of groundwater use. It is simply a matter of resources. I ran a system like that in North Carolina, and just getting things done is a huge issue. A couple of my medium size utility clients have the same problem.
Over the holidays there were a couple articles that came out about groundwater issues in the US, mostly from the declining water level perspective. I also read a paper that suggested that rising sea level had a contribution from groundwater extraction, and of course USGS has maps of areas where the aquifer have collapsed as a result of overpumping. In 2009 USGS published a report that showed a large areas across the country with this issue. The problem is that of the 50,000 community water systems in the US, 500 serve over 50% of the population, and most of them are surface water plants. There are over 40,000 groundwater systems, but most are under 500 customers. Hence, groundwater is under represented at with the larger water associations because the large utilities are primarily surface water, while the small systems are groundwater. AWWA has difficulty reaching the small systems while RWA and NGWA reach out to them specifically. But the small utility seems more oriented to finding and producing water and operating/maintaining/drilling wells than the bigger impact of groundwater use. It is simply a matter of resources. I ran a system like that in North Carolina, and just getting things done is a huge issue. A couple of my medium size utility clients have the same problem.
The bigger picture may contain the largest risk. Changing water supplies is a high cost item. We have seen a couple examples (surface water) as a result of drought. We saw Wichita Falls and Big Springs TX go the potable reuse route due to drought. California is looking at lots of options. Both have had rain lately (Wichita Falls discontinued the potable reuse when the reservoir got to 4% of capacity). Great, but someone is next. Droughts come and go, and the questions is how to deal with them.
Groundwater supposedly is a drought-proof problem, but is it? Groundwater has been a small utility solution, as it has been for agriculture. But aquifer require recharge and water limited areas do not have recharge. The result is a bigger problem – overpumping. Throughout the west/southwest, Plains states, upper Midwest (WI, MN, IA), southeast (SC, NC), we see this issue. Most of these areas have limited surface water so never developed much historically. Rural electrification changes that because it made is easy to put in an electric pump to pull water out of the ground in areas that never had a lot of water on the surface, and hence were not farmed much. Pumps made is easier to farm productively, which led to towns. However, our means to assess recharge are not very good, especially for confined aquifers. The lowering water levels USGS and state agencies see is an indication that recharge is normally over estimated giving a false picture of water availability. If your aquifer declines year after year, it is not drought – it is mining of the aquifer. You are sucking it dry like the eastern Carolinas did. But, like many negative things, there is a lack of willingness to confront the overpumping issue in many areas. There are many states with a lack of regulations on groundwater pumping. And I still think groundwater modeling use is limited to larger utilities, when smaller, rural systems may be most in need of it due to competing interests.
Concurrently, I think there is a tendency to oversell groundwater solutions (ASR, recharge), groundwater quality and the amount of available water (St George, UT). Easy, cheap, limited treatment should not be the only selling point. That leads to some curious decisions like some areas of California north of LA the utilities do not treat hard groundwater – then tell residents they cannot use softeners because of the salt in the wastewater prevents it from being used for reuse. The reason they do not treat – cost, but it makes things difficult for residents. The fact is we do not wish to confront is the realization that for many places, groundwater should probably be the backup plan only, not the primary source.
That leads to the question – what do we do about it when every politician’s goal is for their community to grow? For every farmer to grow more crops? But can they really grow sustainably? DO we not reach a point where there are no more resources to use? Or that the costs are too high? Or that competition become unruly? The growth and groundwater use ship is sailing, but in to many cases they do not see the rocks ahead.

In my last blog I introduced our ethics project we hope to make progress on. But here is one of the interesting questions, especially in Florida. I could not find any actual laws or rules issues here, but it is increasingly common for big engineering contracts to have lawyers, lobbyists, etc. get involved in what is intended to be a qualifications based selection process? There is an interesting issue raised in 287.055 FS (CCNA) where the legal intent is that governmental agencies “shall negotiate a contract with the most qualified firm for professional services at compensation which the agency determines is fair, competitive, and reasonable.” Most states use credentials and qualifications for selection as opposed to cost, because the lowest cost may not get you the best job. You want people doing engineering that have experience with the type of project you are doing. This has come up to me with storage tanks, membrane plans, deep wells, etc. You want someone that has done it before, not someone who is cheaper but hasn’t. There is too much at risk.
In addition the statute is fairly specific about contingent fees (as are most states):
Ch 287.055 (6) PROHIBITION AGAINST CONTINGENT FEES.—
(a) Each contract entered into by the agency for professional services must contain a prohibition against contingent fees as follows: “The architect (or registered surveyor and mapper or professional engineer, as applicable) warrants that he or she has not employed or retained any company or person, other than a bona fide employee working solely for the architect (or registered surveyor and mapper, or professional engineer, as applicable) to solicit or secure this agreement and that he or she has not paid or agreed to pay any person, company, corporation, individual, or firm, other than a bona fide employee working solely for the architect (or registered surveyor and mapper or professional engineer, as applicable) any fee, commission, percentage, gift, or other consideration contingent upon or resulting from the award or making of this agreement.” For the breach or violation of this provision, the agency shall have the right to terminate the agreement without liability and, at its discretion, to deduct from the contract price, or otherwise recover, the full amount of such fee, commission, percentage, gift, or consideration.
So here is the question: As the public becomes more aware of these types of political lobbying activities, does it move the perception of engineers away from a profession and more towards profession toward developers, lawyers and others who are often seen as less ethical than perhaps engineer, doctors, educators, and scientists? And if so, is this good for either the engineering profession or the local governments (and their utilities) involved in the selection process? The comment that “that’s how business get done” is not an acceptable argument when the priority purpose of engineers, and utility operators is the protection of the HEALTH, SAFETY AND WELFARE OF THE PUBLIC. Somehow I think the politicizing of engineering contracts does not help our profession. Looking forward to your thoughts.
 So as 2016 starts, it is time to look at goals for the coming year. I have several project in mind that I would like to make progress on this year. The first is interesting. We have embarked on a project that looks at engineering ethics. The study have several parts:
So as 2016 starts, it is time to look at goals for the coming year. I have several project in mind that I would like to make progress on this year. The first is interesting. We have embarked on a project that looks at engineering ethics. The study have several parts:
One of my reference points is an old publication from ASCE by Murray Mantell, who I got to know about 15 years ago. He wrote such a book in 1964 when he was char of the University of Miami’s Department of Civil Engineering. I believe he has since passed on, but I have used his book in some of my courses.
Other references come from contact with the Board of Professional Engineers in each state and various society’s code of ethics, and historical versions of same. However a “hole” in our project is the perceptions piece. Views change with time and with technology. Things like competition, lobbying, risk and costs create added pressures on engineers and a need to react to those pressures. So what we would like to do is create a survey monkey survey for engineers, professional and not to respond to as a means to evaluate perceptions.
I do not have ready access to a database for this purpose. Gathering data form many states would be difficult as well and duplicative as many engineers have multiple licenses. However, your organization does not have this constraint. So I am reaching out to several societies to see if there is a means to collaborate on this endeavor. The program is as follows:
I am hoping that some of these organizations will find benefit and will agree to participate by emailing the survey link to their members. I will compile the data and we expect to publish it. Most of the work so far is being done via email, and thanks to some prior students for gathering information on it. I have a ways to go here though. So what are your thoughts? If anyone can help with ASCE, NSPE, ACEC, etc, I would appreciate it. And if you get that email with a link, I would appreciate your input and comments.
So everyone is doing their Top 10 questions for 2016 (although with David Letterman off the air, perhaps less so), I figured why not? So it the vein of looking forward to 2016, let’s ponder these issues that could affect utilities and local governments:
Happy New Year everyone. Best to all my friends and followers in 2016!
For the new year, my PUMPS website (not this site) will be undergoing reconstruction. It has been a few years and some things are out of date. Instead the focus will be more on rate studies, financial planning and asset management as opposed to all the other issues (like publications). I will have a separate website for me, with all that stuff since some folks have hit the website looking for it. My main goal is to partner with some folks and try to help smaller utilities with financial and management issues. I will be adding work products, including the asset management stuff we are doing in Dania Beach and Davie. My hope is I energize PUMPS a bit. At the same time via FAU, we will be developing a study of utility costs and revenues since 2005, with emphasis on the impact of the 2008-2009 Recession. This will be instructive – and be an update to the 1997 and 199 studies I did (hard to believe they were so long ago). We will be looking nationally, as well as at different types of treatment, location and size. The idea will be to develop some tools to help utilities benchmark where they are in the bigger picture, and to help with identifying trends and potential missing issues. COnncection rates and asset is improtant to insure hte timely renewal and repalcement of critical infrastrucutre. After all, the people who get fired when things go wrong with a utility are not the politicians – its us!. I will be solicitng (or my studnet will) data from over 300 utilities across the country. If you are interested, or have clients who might be, let me know. I have tnatively discussed publication with AWWA – but it won’t jsut be water. Resue, wastewater etc will be included. Should be fun! Look for the results next summer!!