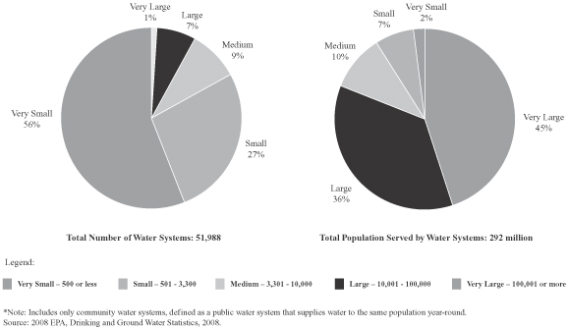
My last blog was a discussion about surpluses. The State of Florida will have a $1.3 billion surplus this year and a host of politically expedient answers for where that money goes (tax cuts, pork projects, projects to help election results), but little mention of replenishing trust funds and reserves that were emptied to balance the budget amid tax cuts from 2010 – 2012. But perhaps it is not the legislators or their constituents that we should blame for not understanding the need for reserves because the truth is that most people are not used to saving. A recent article I read noted that 72 percent of Americans live paycheck to paycheck and would have difficulty putting $2000 together if needed. $2000 is not a lot of money these days – it won’t buy you a transmission for example or a new engine for your car. It won’t cover first, last and a deposit on a rental. And it won’t cover the down payment on a house or most cars. There are people who do not receive enough income to achieve some degree of savings, but not 72% of us. We have come to perceive that having little savings is normal, but it wasn’t always this way and it is not this way everywhere in the world. Back in the day, American saved more than they do now. The reason is not that they had more money (they didn’t) or that they had less to spend money on (as things cost more proportionately). But it was that “rainy day” they all knew would come and when they would need money. They had been through depressions, recession and losses of industries (remember those Concord coachmakers did not get a federal bailout in trying to compete with Henry Ford). They knew that there would be times when they needed to rely on themselves to survive and savings was the key.
There are two major differences from the past. The most important is the fact is that credit was a lot harder to come by back in the day, so you needed cash for those big purchases. That has changed dramatically in 50 years. Today we get advertisements for credit cards – in the mail, instant credit at stores, easy credit for cars, and in the early 2000s, no-money-down-no-income-verification loans on real estate. The need to save evaporated. The access to easy credit has eliminated much of the need to save for those big expenses. We can borrow to acquire them. If we have a job problem, we borrow against the house or life insurance policy. These are good backstops that help us maintain our way of life.
At the same time as we are being extended opportunities to secure funds to spend, we are barraged by advertisements and flyers and pitches to spend that money on products and services, many of which we probably don’t need, but are “cool” to have. We are encouraged to compete to have better “stuff” than the other guy, and make sure we have the newest technology. We all do it. Just look at all phones can do, while keeping in mind that the old Bell phone I bought in college still works regardless of the situation and still sounds good. No cool ringtones however, nor photo capability. All that means we spend less on “needs” and more on “stuff.”
Given this backdrop it is no surprise the attitude of decision-makers in government toward revenues and expenses. Re-education of the public is needed as opposed to rhetoric. We need to move the public discussion away from the concept of a balanced budget being expenses equal revenues to the correct concept of revenues + reserve expenses = expenses plus savings. At times you use reserves (and savings =0) while other times reserve expenses are 0, while savings are positive. When big expenses come, borrow, but recurring expenses should not be funded through borrowing (credit). We should seek to avoid is the desire to cut taxes (akin to cutting our salaries) to bring the budget back into balance that if we run a surplus, or spend it on “stuff.” Such a system leaves room for those lean times when revenues may fluctuate but expenses do not (or increase).