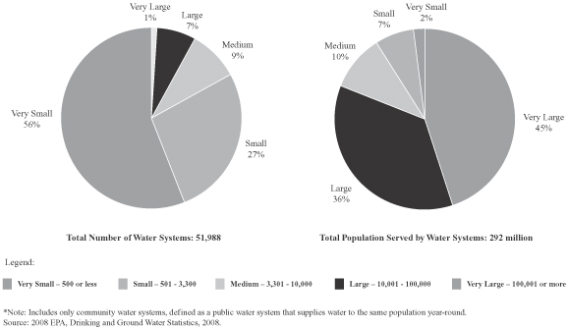
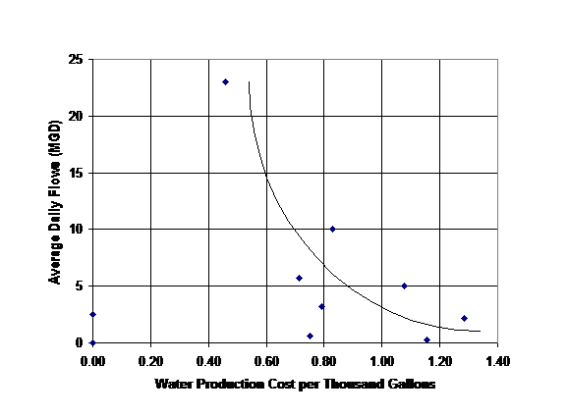
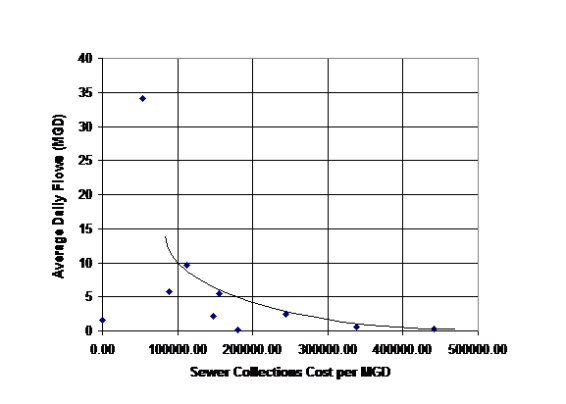
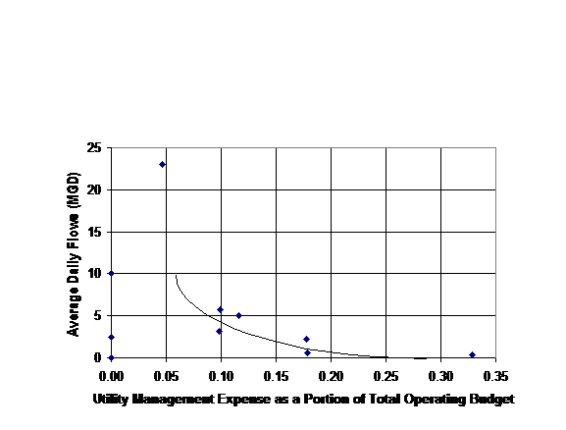
We all know that our infrastructure is deteriorating. Deferred maintenance increases the risk of system failure. The need for capital reinvestment within the utility industry has historically been very low. As a result, in its “2013 Report Card for America’s Infrastructure,” the American Society of Civil Engineers assigned a grade of “D” to America’s drinking water systems, citing billions of dollars of annual funding shortfalls to replace aging facilities near the end of their useful lives and to comply with existing future federal water regulations (ASCE, 2013). AWWA estimates that investments of at least $1 trillion are needed over the next 25 years.
While a pay-as-you-go capital funding seems like the best way to go, that is difficult to accomplish with the large outlays needed to upgrade the infrastructure system and the controls on rates often exercised by local officials. As a result, borrowing is required and the condition of infrastructure and the lack of reserves are a part of how the utility is viewed by those who lend monies. Utility managers need to understand how the lending agencies evaluate risk.
Lenders use many tests. Among them are: whether the utility’s annual depreciation expense is used of accumulated as reinvestment in the system, whether adequate reserves are present, whether annual capital spending that is below the amount of annual depreciation and the amount of revenues in excess of projected debt (debt service coverage). The target debt service coverage may depend upon the requirements of the underwriter, the rating agencies and the investors. Debt service coverage could be as low as 15% or as high as 50%. In 2012, the median all-in annual debt service coverage excluding connection fees for utilities rated “AAA” by Fitch Ratings was 220%, while the median for AA-rated and A-rated utilities was 180% and 140%, respectively. (Fitch, 2012).
A working capital target of 90 days of rate revenue is a minimum, but since 2008, more is likely to be required depending on the size of the system and the history of revenues. Where the revenues were stable despite 2008, less may be required. For those utilities that suffered major decreases, reserves should be far larger – perhaps a year or more. Other criteria that could be used to evaluate the projects when borrowing money include public health and safety, regulatory compliance, system reliability, the risk and consequences of asset failure, redundancy, community/customer benefit and sustainability. At the same time, the expectation is that the utility systems that retain all monies in the system to be utilized to improve the system and pay for debt service, except those used for the purchase of indirect services from the General Fund that are justified with indirect cost studies.
Despite the above, rate are an issue. Fitch Ratings has indicated that it considers rates for combined water and wastewater service that are higher than 2% of the median household income – or 1% for an individual water or wastewater utility – to be financially burdensome (Fitch, 2012). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) considers that rates for an individual water or wastewater utility that are greater than 2% of median household income may have a high financial impact on customers. (EPA, 1997). Utilities with a stronger financial profile might have residential charges for combined water and wastewater service that are less than or equal to 1.2% of median household income, or less than or equal to 0.6% for an individual water or wastewater utility. All revenues generated through system operations generally must remain within the system and can only be used for lawful purposes of the system.
Canadian utilities employ more formal polices to establish fiscal policies to provide reserves to insure stability in the event of unforeseen circumstances. Reserve targets focus on ensuring liquidity in the event there is an interruption in funding, increased capital costs due to new regulatory requirements or a short term funding emergency – all the issues evaluated by the bankers. Reserve targets are policy decisions. Benchmarking is an evolving practice within Canadian public sector utilities particularly as it relates to financial planning and capital financing. The benchmarking exercise provides valuable information to help assess fiscal performance, the needs of customers, and provide the tools to help support optimum performance.