June was a tough month and looking back I realize I really didn’t post. I was in Chicago, spent 2 weeks with middle schoolers, prepared my promotion package, god the doors completed on the house, etc. and suddenly it was the 4th of July. Yikes time flies. But it was interesting. Here I want to talk a little about Chicago.
I went to Chicago to do a 3 day, 12 hour class with elected officials. Most are board members for their local utility, but they went from a small South Carolina system to San Antonio and St. Paul. A huge variety. And we learned a lot. Obviously the Flint crisis was on their minds. But I thought the most interesting thing was that these folks understood what happened. I asked what they thought the real issue was in Flint and the resounding answer was – politics. Bad decision-making. Poor preparation. Notably, not lead service lines. These people got it. They read behind the headlines. Of course these are the officials that wanted to learn more about their water and sewer systems, as opposed to the many that do not take the time to, but interesting nonetheless.
Another issue was talked about was finances. I ask them to bring their budget, water use, pipelines, etc. The goal is to do a quick comparison between systems and then discuss what it means (if anything). I have started doing the exercise each year and we find the same thing – smaller systems cost more per thousand gallons to run than larger systems, so hence their rates must be higher or they are not doing repairs and replacements on a timely basis. This group got that as well and understood that comparisons of their system to others needed to be carefully vetted. No two system are alike, but size, treatment, terrain can all affect costs to the customer.
We also talked about leadership. I am applying for an AWWA project on leadership, but when asked, these folks had some great answers. They see leadership as a personal trait (inspiration, vision) as well as being driven by event (negotiating crisis or change), and having the ability to bring people along through the rough patches. Leadership is an issue that needs more exploration, but I thought this was a good start to preface the larger survey I hope to do for AWWA’s members.
In the meantime, I learned a lot about the Chicago River bridges, enjoyed the planetarium, a Cubs night game, Millenium Park and a walk along the waterfront. Very cool.







 s:
s: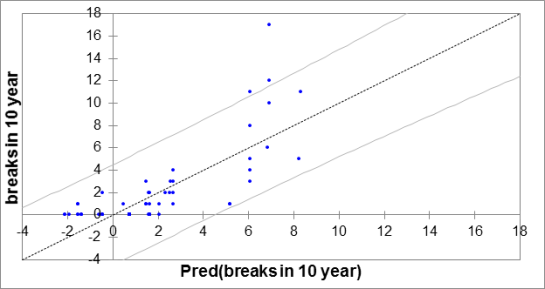
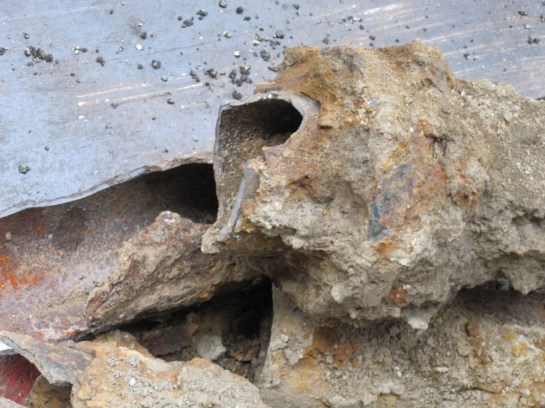


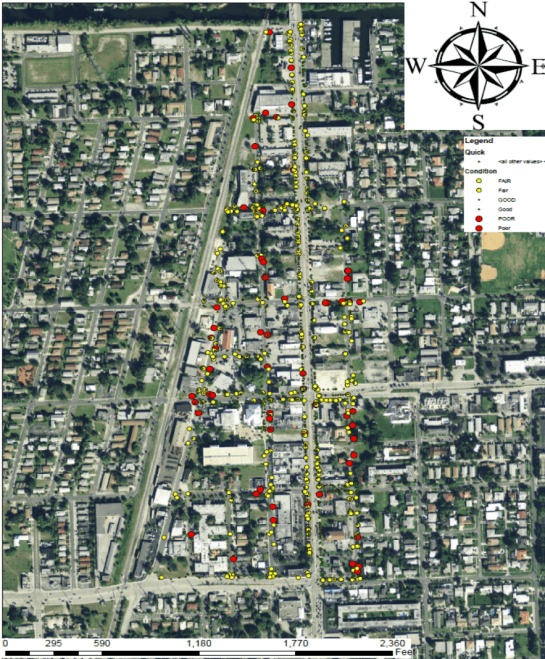













 Florida Atlantic University is hosting the first Arctic-Florida Symposium next week (May 3-5). This is a big event and should prove interesting I will be speaking. The idea is to evaluate the arctic and Florida and open some dialogue. Florida and Alaska would seem to be opposites when it comes to many things. Alaska is cold; Florida is the land of eternal summer. Alaska has snow and blizzards; Florida has tropical storms with pounding rain. Sea Level rise is a critical concern to much of Florida’s coast, but much of Alaska’s coast is mountains. Temperatures affect the permafrost in Alaska, but heat is not new in Florida, where permafrost has not existed in millions of years, if ever. So how are these two states, located over 5000 miles apart, similar? That was the question posed before the Arctic-Florida conference in 2016. The result was that Alaska and Florida share many commonalities, and there is much to learn from each other. For example, population migration is at hand in Alaska. It is in Florida’s future. Likewise diseases have impacted at risk areas in Alaska, portending a potential future condition for southeast Florida. Adaptation strategies are underway in Florida, which can help in Alaska. Roads, water supplies, water storage, wastewater and storm water are all issues that pose challenges to both states, so there are answers in infrastructure adaptation strategies. Many common problems can be solved by sharing information. The Florida–Alaska connection is an example of looking outside the box to find ideas that can be useful to those deemed to be far different. More to come on this….
Florida Atlantic University is hosting the first Arctic-Florida Symposium next week (May 3-5). This is a big event and should prove interesting I will be speaking. The idea is to evaluate the arctic and Florida and open some dialogue. Florida and Alaska would seem to be opposites when it comes to many things. Alaska is cold; Florida is the land of eternal summer. Alaska has snow and blizzards; Florida has tropical storms with pounding rain. Sea Level rise is a critical concern to much of Florida’s coast, but much of Alaska’s coast is mountains. Temperatures affect the permafrost in Alaska, but heat is not new in Florida, where permafrost has not existed in millions of years, if ever. So how are these two states, located over 5000 miles apart, similar? That was the question posed before the Arctic-Florida conference in 2016. The result was that Alaska and Florida share many commonalities, and there is much to learn from each other. For example, population migration is at hand in Alaska. It is in Florida’s future. Likewise diseases have impacted at risk areas in Alaska, portending a potential future condition for southeast Florida. Adaptation strategies are underway in Florida, which can help in Alaska. Roads, water supplies, water storage, wastewater and storm water are all issues that pose challenges to both states, so there are answers in infrastructure adaptation strategies. Many common problems can be solved by sharing information. The Florida–Alaska connection is an example of looking outside the box to find ideas that can be useful to those deemed to be far different. More to come on this…. Curtailed water use and conservation are common topics of conversation in areas with water supplies limitations. As drought conditions worsen, the need for action increases, so when creating a regulatory framework, or when trying to measure water use efficiency, water supply managers often look for easily applied metrics to determine where water use can be curtailed. Unfortunately, the one-size-fits-all mentality comes with a potential price of failing to fully grasp the consequences decision-making based on such metrics.
Curtailed water use and conservation are common topics of conversation in areas with water supplies limitations. As drought conditions worsen, the need for action increases, so when creating a regulatory framework, or when trying to measure water use efficiency, water supply managers often look for easily applied metrics to determine where water use can be curtailed. Unfortunately, the one-size-fits-all mentality comes with a potential price of failing to fully grasp the consequences decision-making based on such metrics. A week or so ago, on a Sunday afternoon, I flew across Middle America to Colorado for a meeting and was again struck by the crop circles that dominate the landscape west of the Mississippi River. They are everywhere and are a clear sign of unsustainable groundwater use. I recently participated in a fly in event for National Groundwater Association in Washington DC, where several speakers, including myself, talked about dwindling groundwater levels and the impact of agriculture, power and economies. The impact is significant. Dr. Leonard Konikow, a recently retired USGS scientist, noted that he thinks a portion of sea level rise is caused by groundwater running off agriculture and from utilities and making its way to the ocean. He indicated that 5% of SLR each year was caused by groundwater runoff, and has upped his estimates in the past 10 years to 13%. This is because it is far easier for water to runoff the land than seep into rocks, especially deep formations that may take many years to reach the aquifer. And since ET can reach 4 ft below the surface, many of the western, dry, hot areas lose most of this water during the summer months. Hence the impact to agriculture, and the accompanying local communities and their economies will be significant.
A week or so ago, on a Sunday afternoon, I flew across Middle America to Colorado for a meeting and was again struck by the crop circles that dominate the landscape west of the Mississippi River. They are everywhere and are a clear sign of unsustainable groundwater use. I recently participated in a fly in event for National Groundwater Association in Washington DC, where several speakers, including myself, talked about dwindling groundwater levels and the impact of agriculture, power and economies. The impact is significant. Dr. Leonard Konikow, a recently retired USGS scientist, noted that he thinks a portion of sea level rise is caused by groundwater running off agriculture and from utilities and making its way to the ocean. He indicated that 5% of SLR each year was caused by groundwater runoff, and has upped his estimates in the past 10 years to 13%. This is because it is far easier for water to runoff the land than seep into rocks, especially deep formations that may take many years to reach the aquifer. And since ET can reach 4 ft below the surface, many of the western, dry, hot areas lose most of this water during the summer months. Hence the impact to agriculture, and the accompanying local communities and their economies will be significant.